Date:Sep 2, 2024
Abdolreza Iesvand Heidari
Explanation and Comparison with Market Conditions:
Early 2000s: The risk values are negative, indicating a period of difficulty for SVB, which aligns with the dot-com bubble burst (2000-2002). Many tech startups, SVB’s primary clientele, faced severe challenges during this time.
2008 Financial Crisis: There’s a significant drop in the risk value in 2008 (-5.02), reflecting the broader financial crisis that severely impacted banks worldwide. However, the risk value sharply increases to a positive 3.67 in 2009, suggesting a strong recovery or adjustments SVB made during that period.
Post-Crisis Recovery: From 2010 onwards, the risk fluctuates but remains relatively low, with occasional positive values in 2013, 2016, 2017, and 2020, suggesting periods of profitability or reduced risk.
2021-2022: The sharp drop in the risk value in 2021 (-6.99) and 2022 (-4.42) could be linked to the bank’s exposure to high-risk ventures, the impact of rising interest rates, and broader market instability, eventually leading to its collapse in 2023.
Real-World Implications:
Interest Rate Risks: The negative trend in 2021-2022 aligns with the period when the Federal Reserve began raising interest rates, which negatively impacted SVB’s bond portfolio and liquidity position.
Market Volatility: The tech sector’s volatility and SVB’s concentrated exposure to this sector likely exacerbated the risk in the final years.
Liquidity Crisis: The significant negative risk in the years leading up to SVB’s collapse suggests increasing challenges in managing liquidity and balancing high-risk assets with obligations, ultimately leading to insolvency.This chart visually represents the increasing risk that culminated in the bank’s collapse, highlighting how external economic factors and internal vulnerabilities converged to create an unsustainable situation for SVB.
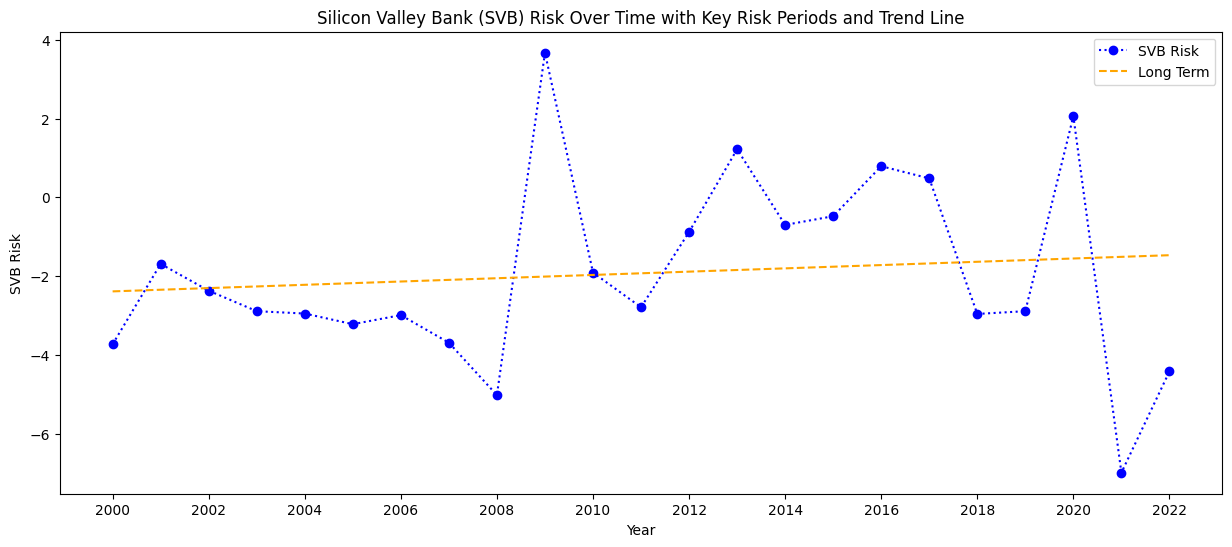
The long-term trend in Silicon Valley Bank’s risk profile shows significant fluctuations over the years. During the dot-com bubble and the 2007-2008 financial crisis, risk values surged, indicating periods of substantial financial stress. After 2008, while there was some recovery and stabilization, risk levels remained volatile with continued periods of uncertainty. Recent years, particularly during the interest rate hikes, have seen a resurgence in risk, underscoring ongoing challenges and volatility in SVB’s financial environment. The trend line highlights an overall pattern of considerable variability with distinct periods of increased risk.







